Chess Game Movements: Rules and Strategies
Chess is a strategic game played between two opponents on an 8×8 checkered board. The game involves six types of pieces—each with distinct movements and roles. Understanding the movements of each piece is fundamental to mastering the game. This article explains the movement rules for each piece and highlights key strategies to enhance gameplay.
The Chess Pieces and Their Movements
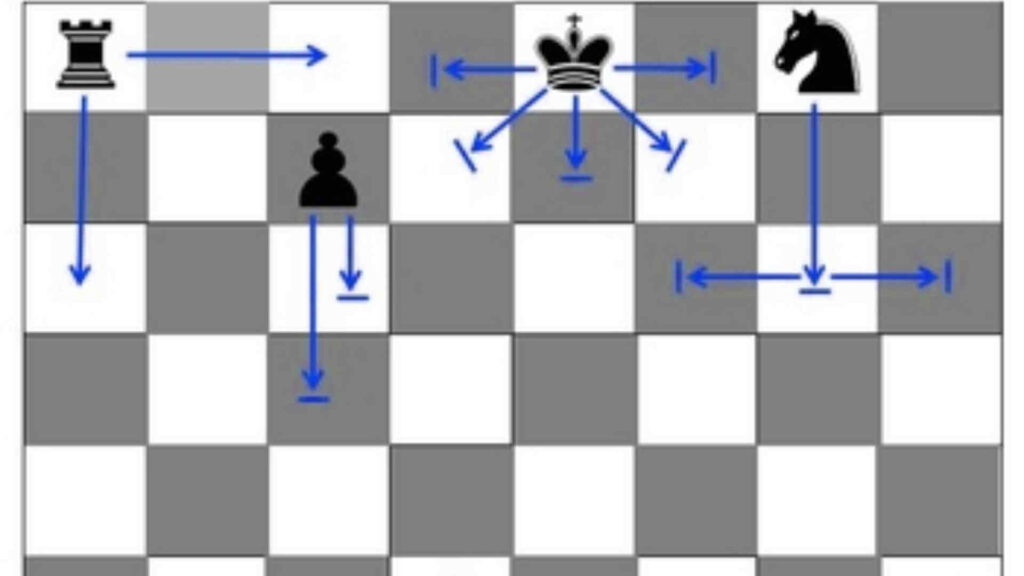
- King:
- Moves one square in any direction—horizontally, vertically, or diagonally.
- Special Move: Castling, where the king moves two squares toward a rook, and the rook jumps over the king. This move improves king safety and rook mobility.
- Queen:
- Moves any number of squares in any direction—horizontally, vertically, or diagonally.
- It is the most powerful piece due to its range of movement.
- Rook:
- Moves any number of squares horizontally or vertically.
- Often used to control open files and ranks.
- Bishop:
- Moves any number of squares diagonally.
- Each bishop stays on the color of squares it started on—either light or dark.
- Knight:
- Moves in an ‘L’ shape—two squares in one direction and then one square perpendicular.
- It is the only piece that can jump over other pieces.
- Pawn:
- Moves forward one square but captures diagonally.
- Special Moves:
- Double Move: On its first move, a pawn can advance two squares.
- En Passant: A pawn can capture an adjacent pawn that moves two squares forward.
- Promotion: When a pawn reaches the opponent’s back rank, it can be promoted to any piece except a king (usually promoted to a queen).
Special Chess Movements
- Castling:
- Conditions:
- Neither the king nor the rook involved has moved before.
- No pieces are between the king and rook.
- The king is not in check, and no squares it passes through are under attack.
- Purpose: Improves king safety and activates the rook.
- Conditions:
- En Passant:
- Allows a pawn to capture an opponent’s pawn if it moves two squares forward and lands beside the capturing pawn.
- Must be done immediately after the opposing pawn moves.
- Promotion:
- Occurs when a pawn reaches the last rank of the board.
- Players typically promote to a queen due to its strength.
Basic Strategies Using Piece Movements
- Control the Center:
- Move pawns and pieces to dominate central squares (e4, d4, e5, d5) to gain board control.
- Develop Pieces Quickly:
- Move knights and bishops early to active squares to prepare for attacks.
- King Safety:
- Castle early to protect the king and connect rooks.
- Open Files and Diagonals:
- Use rooks and bishops to control open lines for long-range attacks.
- Tactics with Knights:
- Knights excel at creating forks—attacking two pieces simultaneously.
Endgame Movements and Techniques
- King Activity:
- In the endgame, activate the king to support pawns and threaten enemy pieces.
- Pawn Promotion:
- Push pawns to promote them into queens and increase attacking power.
- Checkmating Patterns:
- Use combinations like rook and king or queen and king to trap the opposing king.
Common Mistakes with Piece Movements
- Leaving Pieces Unprotected:
- Avoid placing pieces in vulnerable positions without support.
- Overextending Pawns:
- Moving pawns too far can create weaknesses and expose the king.
- Ignoring Development:
- Focusing only on one piece instead of mobilizing multiple pieces.
Modern Tools for Practicing Movements
Online platforms like Chess.com and Lichess offer interactive puzzles and simulations to practice piece movements and strategies. Chess engines like Stockfish analyze moves and suggest improvements, helping players refine their skills.
Conclusion
Mastering chess movements is essential for building strategies and executing tactics effectively. Each piece has unique movements that influence the dynamics of the game. From basic moves to special rules like castling and promotion, understanding and practicing these movements can elevate your gameplay. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced player, continuous practice and analysis will help you improve your performance and appreciation of chess.